Converters and encryption - Java SDK
Temporal's security model is designed around client-side encryption of Payloads. A client may encrypt Payloads before sending them to the server, and decrypt them after receiving them from the server. This provides a high degree of confidentiality because the Temporal Server itself has absolutely no knowledge of the actual data. It also gives implementers more power and more freedom regarding which client is able to read which data -- they can control access on keys, algorithms, etc.
A Temporal developer adds client-side encryption of Payloads by providing a Custom Payload Codec to its Client. Depending on business needs, a complete implementation of Payload Encryption may involve the selection of appropriate encryption algorithms, management of encryption keys, and/or restriction a subset of their users from viewing payload output.
The server itself never adds encryption over Payloads. Therefore, unless client-side encryption is implemented, Payload data will be persisted in non-encrypted form to the data store, and any Client that can make requests to a Temporal namespace (including the Temporal UI and CLI) will be able to read Payloads contained in Workflows. When working with sensitive data, you should always implement Payload encryption.
Custom Payload Codec in Java
How to create a custom Payload Codec using the Java SDK.
Create a custom implementation of PayloadCodec and use it in CodecDataConverter to set a custom Data Converter.
The Payload Codec does byte-to-byte conversion and must be set with a Data Converter.
Define custom encryption/compression logic in your encode method and decryption/decompression logic in your decode method.
The following example from the Java encryption sample shows how to implement encryption and decryption logic on your payloads in your encode and decode methods.
class YourCustomPayloadCodec implements PayloadCodec {
static final ByteString METADATA_ENCODING =
ByteString.copyFrom("binary/encrypted", StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
private static final String CIPHER = "AES/GCM/NoPadding";
// Define constants that you can add to your encoded Payload to create a new Payload.
static final String METADATA_ENCRYPTION_CIPHER_KEY = "encryption-cipher";
static final ByteString METADATA_ENCRYPTION_CIPHER =
ByteString.copyFrom(CIPHER, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
static final String METADATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY_ID_KEY = "encryption-key-id";
private static final Charset UTF_8 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
// See the linked sample for details on the methods called here.
@NotNull
@Override
public List<Payload> encode(@NotNull List<Payload> payloads) {
return payloads.stream().map(this::encodePayload).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@NotNull
@Override
public List<Payload> decode(@NotNull List<Payload> payloads) {
return payloads.stream().map(this::decodePayload).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private Payload encodePayload(Payload payload) {
String keyId = getKeyId();
SecretKey key = getKey(keyId);
byte[] encryptedData;
try {
encryptedData = encrypt(payload.toByteArray(), key); // The encrypt method contains your custom encryption logic.
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new DataConverterException(e);
}
// Apply metadata to the encoded Payload that you can verify in your decode method before decoding.
// See the sample for details on the metadata values set.
return Payload.newBuilder()
.putMetadata(EncodingKeys.METADATA_ENCODING_KEY, METADATA_ENCODING)
.putMetadata(METADATA_ENCRYPTION_CIPHER_KEY, METADATA_ENCRYPTION_CIPHER)
.putMetadata(METADATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY_ID_KEY, ByteString.copyFromUtf8(keyId))
.setData(ByteString.copyFrom(encryptedData))
.build();
}
private Payload decodePayload(Payload payload) {
// Verify the incoming encoded Payload metadata before applying decryption.
if (METADATA_ENCODING.equals(
payload.getMetadataOrDefault(EncodingKeys.METADATA_ENCODING_KEY, null))) {
String keyId;
try {
keyId = payload.getMetadataOrThrow(METADATA_ENCRYPTION_KEY_ID_KEY).toString(UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PayloadCodecException(e);
}
SecretKey key = getKey(keyId);
byte[] plainData;
Payload decryptedPayload;
try {
plainData = decrypt(payload.getData().toByteArray(), key); // The decrypt method contains your custom decryption logic.
decryptedPayload = Payload.parseFrom(plainData);
return decryptedPayload;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new PayloadCodecException(e);
}
} else {
return payload;
}
}
private String getKeyId() {
// Currently there is no context available to vary which key is used.
// Use a fixed key for all payloads.
// This still supports key rotation as the key ID is recorded on payloads allowing
// decryption to use a previous key.
return "test-key-test-key-test-key-test!";
}
private SecretKey getKey(String keyId) {
// Key must be fetched from KMS or other secure storage.
// Hard coded here only for example purposes.
return new SecretKeySpec(keyId.getBytes(UTF_8), "AES");
}
//...
}
Set Data Converter to use custom Payload Codec
Use CodecDataConverter with an instance of a Data Converter and the custom PayloadCodec in the WorkflowClient options that you use in your Worker process and to start your Workflow Executions.
For example, to set a custom PayloadCodec implementation with DefaultDataConverter, use the following code:
WorkflowServiceStubs service = WorkflowServiceStubs.newLocalServiceStubs();
// Client that can be used to start and signal Workflows
WorkflowClient client =
WorkflowClient.newInstance(
service,
WorkflowClientOptions.newBuilder()
.setDataConverter(
new CodecDataConverter(
DefaultDataConverter.newDefaultInstance(),
Collections.singletonList(new YourCustomPayloadCodec()))) // Sets the custom Payload Codec created in the previous example with an instance of the default Data Converter.
.build());
- Data encoding is performed by the client using the converters and codecs provided by Temporal or your custom implementation when passing input to the Temporal Cluster. For example, plain text input is usually serialized into a JSON object, and can then be compressed or encrypted.
- Data decoding may be performed by your application logic during your Workflows or Activities as necessary, but decoded Workflow results are never persisted back to the Temporal Cluster. Instead, they are stored encoded on the Cluster, and you need to provide an additional parameter when using the temporal workflow show command or when browsing the Web UI to view output.
For reference, see the Encryption sample.
Using a Codec Server
A Codec Server is an HTTP server that uses your custom Codec logic to decode your data remotely.
The Codec Server is independent of the Temporal Cluster and decodes your encrypted payloads through predefined endpoints.
You create, operate, and manage access to your Codec Server in your own environment.
The temporal CLI and the Web UI in turn provide built-in hooks to call the Codec Server to decode encrypted payloads on demand.
Refer to the Codec Server documentation for information on how to design and deploy a Codec Server.
For reference, see the Codec server sample.
Using custom Payload conversion
How to do custom Payload conversion using the Java SDK.
Temporal SDKs provide a Payload Converter that can be customized to convert a custom data type to Payload and back.
Implementing custom Payload conversion is optional. It is needed only if the default Data Converter does not support your custom values.
To support custom Payload conversion, create a custom Payload Converter and configure the Data Converter to use it in your Client options.
The order in which your encoding Payload Converters are applied depend on the order given to the Data Converter. You can set multiple encoding Payload Converters to run your conversions. When the Data Converter receives a value for conversion, it passes through each Payload Converter in sequence until the converter that handles the data type does the conversion.
Payload Converters can be customized independently of a Payload Codec. Temporal's Converter architecture looks like this:
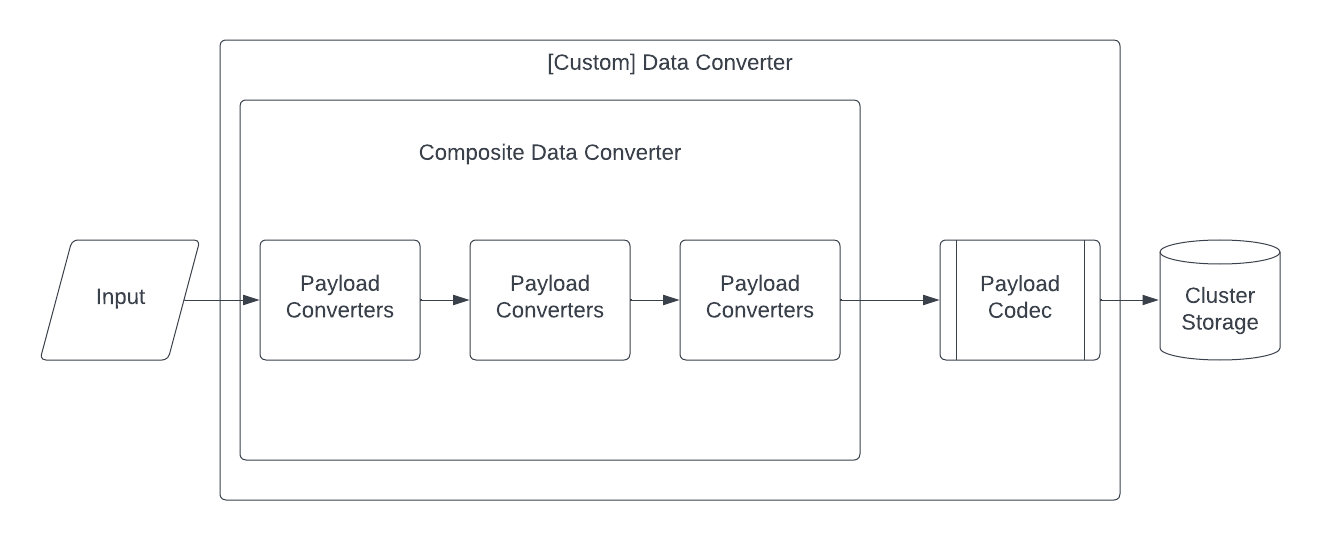
Create a custom implementation of a PayloadConverter interface and use the withPayloadConverterOverrides method to implement the custom object conversion with DefaultDataConverter.
PayloadConverter serializes and deserializes method parameters that need to be sent over the wire.
You can create a custom implementation of PayloadConverter for custom formats, as shown in the following example:
/** Payload Converter specific to your custom object */
public class YourCustomPayloadConverter implements PayloadConverter {
//...
@Override
public String getEncodingType() {
return "json/plain"; // The encoding type determines which default conversion behavior to override.
}
@Override
public Optional<Payload> toData(Object value) throws DataConverterException {
// Add your convert-to logic here.
}
@Override
public <T> T fromData(Payload content, Class<T> valueClass, Type valueType)
throws DataConverterException {
// Add your convert-from logic here.
}
//...
}
You can also use specific implementation classes provided in the Java SDK.
For example, to create a custom JacksonJsonPayloadConverter, use the following:
//...
private static JacksonJsonPayloadConverter yourCustomJacksonJsonPayloadConverter() {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// Add your custom logic here.
return new JacksonJsonPayloadConverter(objectMapper);
}
//...
To set your custom Payload Converter, use it with withPayloadConverterOverrides with a new instance of DefaultDataConverter in your WorkflowClient options that you use in your Worker process and to start your Workflow Executions.
The following example shows how to set a custom YourCustomPayloadConverter Payload Converter.
//...
DefaultDataConverter ddc =
DefaultDataConverter.newDefaultInstance()
.withPayloadConverterOverrides(new YourCustomPayloadConverter());
WorkflowClientOptions workflowClientOptions =
WorkflowClientOptions.newBuilder().setDataConverter(ddc).build();
//...